
But this approach can be highly unsatisfactory, even when sampling from a perfectly symmetric distribution. 9–11).Īnother seemingly natural but unsatisfactory approach to estimating the probability density function is to assume observations are sampled from a normal curve and replace the population mean and variance (μ and σ 2) in Equation (2.10) with the sample mean and variance ( X ¯ and s 2 ). A histogram provides a crude estimate, but for various reasons it can be unsatisfactory (e.g., Silverman, 1986, pp. For some purposes to be covered, it is useful to have an estimate of f( x) (the equation for the probability density function) based on observations we make. An example is Equation (2.10), which gives the equation for the probability density function of the normal distribution. The equation for this curve is typically labeled f( x). Wilcox, in Applying Contemporary Statistical Techniques, 2003 3.7 Kernel Density EstimatorsĪs indicated in Section 2.6, probabilities associated with continuous variables are determined by the area under a curve called a probability density function. These characteristics make the range nearly useless for inferential purposes. Worst of all, the range in a sample of data does not estimate any property of the population, because for most distributions (including the normal), the population range is infinite.

It is also sensitive to atypical values (outliers) and to the total sample size, increasing with increasing number of observations. Relying on two extreme observations, the range does not take into account the rest of the scores (see Figure 1). While the range of a particular distribution may be useful for learning about the distance between the smallest and the largest values, the drawbacks are evident. In comparison, in a different distribution of scores (71, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, and 98), the range would still be the same (27) – as the minimum and the maximum do not change – although scores in between are much closer to each other. For example, in the following distribution of math scores ordered from the smallest to the highest (71, 75, 79, 86, 90, 94, 96, and 98), the range would be X max − X min = 98 − 71 = 27. The range is the simplest way to describe a set of test scores: Subtract the smallest X min from the largest X max value. Interquartile Range vs.Most commonly, the dispersion of a variable is summarized quantitatively in statistics such as range, interquartile range (IQR), variance, and standard deviation. #calculate interquartile range of 'var1', 'var2', and 'var4' columns

#INTERQUARTILE RANGE HOW TO#
The following code shows how to calculate the interquartile range of several columns in a data frame: #define data frame 1 Example 4: Interquartile Range of Several Columns in Data Frame #calculate interquartile range of 'var1' column

The following code shows how to calculate the interquartile range of a specific column in a data frame: #define data frame If your vector has missing values, be sure to specify na.rm=TRUE to ignore missing values when calculating the interquartile range: #define vector with some missing values #calculate interquartile range of values in vectorĮxample 2: Interquartile Range of a Vector with Missing Values The following code shows how to calculate the interquartile range of values in a vector: #define vector Example 1: Interquartile Range of a Vector The following examples show how to use this function in practice. We can use the built-in IQR() function to calculate the interquartile range of a set of values in R: IQR(x)
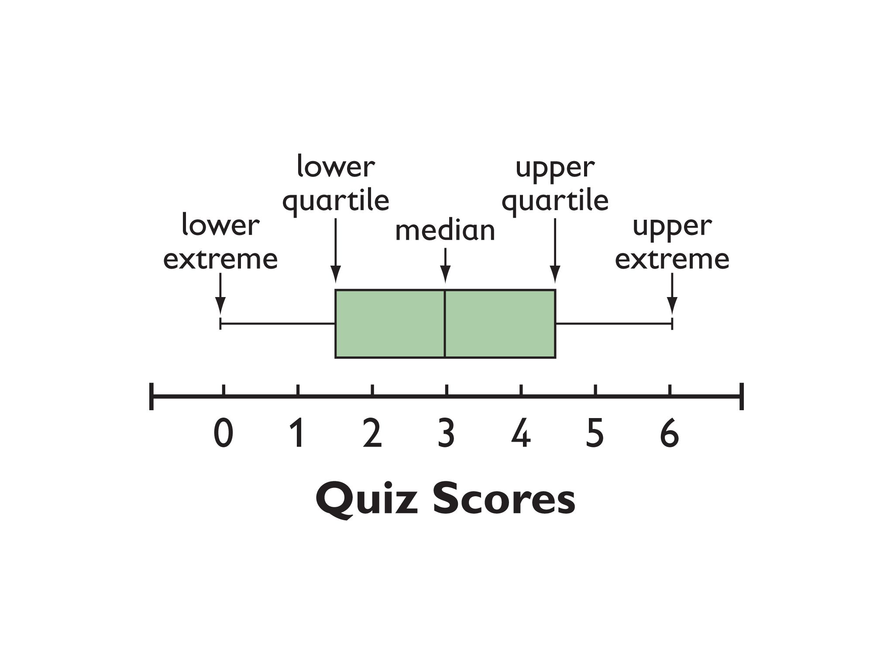
In simple terms, it measures the spread of the middle 50% of values. The interquartile range represents the difference between the first quartile (the 25th percentile) and the third quartile (the 75th percentile) of a dataset.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
